Federal Funding
Federal Motor Fuel Taxes
The motor fuel tax is a per-gallon excise tax levied on gasoline, diesel, and other special fuels, and is deposited into the Federal Highway Trust Fund (HTF). Motor fuel taxes provide the majority of the revenue used for Federal surface transportation funding.
The HTF was established by the Federal-aid Highway Act of 1956 for the direct purpose of funding the construction of an Interstate Highway System and aiding in the finance of primary, secondary, and urban routes. Prior to establishment of the HTF, a federal motor fuel tax of 1 cent per gallon was enacted in 1932 and increased, extended, and rescinded multiple times until 1955. Revenue was not collected in a dedicated fund, but instead was pooled with the General Fund of the Treasury. Similarly, cash to pay for obligations incurred for the Federal highway program came from the General Fund.
Initially set at 3 cents per gallon in 1956, the motor fuel tax was increased to 4 cents per gallon in 1959. Then after a 24-year hiatus, motor fuel taxes were increased to 9 cents per gallon in 1983 and a new dedicated Mass Transit Account was established alongside the existing Highway Account and was funded with one-ninth of the revenues coming into the HTF. The next year, the motor fuel tax on diesel fuel was increased separately by 6 cents per gallon, a differential that remains today.
Since 1987, except from January 1996 to October 1997, an additional 0.1 cent per gallon has been levied and deposited in the Leaking Underground Storage Tank Trust Fund.
In 1990, a 5-cent increase was passed as part of the Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act, raising the Federal motor fuel tax to 14 cents per gallon for gasoline and 20 cents per gallon for diesel fuel. However, this legislation also directed half of the increase to the General Fund of the Treasury for deficit reduction. A final fuel tax increase of 4.3 cents per gallon was enacted in 1993 to further aid in deficit reduction, bringing the motor fuel tax to its current level of 18.3 cents per gallon for gasoline and 24.3 cents per gallon for diesel fuel. This bill ended the redirection of 2.5 cents to the General Fund in 1995, but instead, the 4.3-cent increase was used for deficit reduction until the Taxpayers Relief Act of 1997 ended that provision. The current tax rates on motor fuels are shown in the table.
| Distribution of Tax | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Excise Tax | Tax rate (cents) | Highway Account | Mass Transit Account |
| Gasoline1 | 18.3 per gallon | 84% | 16% |
| Diesel 1 | 24.3 per gallon | 88% | 12% |
| Gasohol 1 | 18.3 per gallon | 84% | 16% |
| Liquefied petroleum gas | 18.3 per gallon | 88% | 12% |
| Liquefied natural gas | 24.3 per gallon | 92% | 8% |
| Compressed natural gas | 18.3 per gallon | 93% | 7% |
1 In addition to these rates, a 0.1-cent per gallon tax is levied and deposited in the Leaking Underground Storage Tank Trust Fund.
Collection
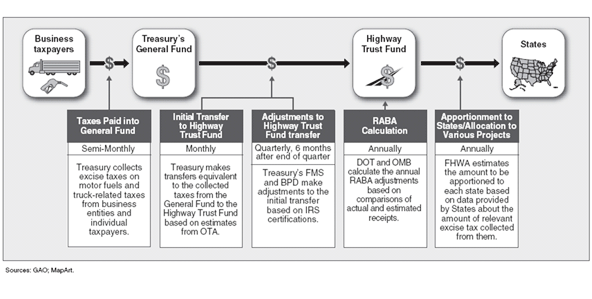
Most of the excise taxes credited to the HTF are not collected directly from the consumer. Instead, they are paid to the Internal Revenue Service by the producer or importer of the taxable product. User taxes are deposited in the General Fund of the Treasury, and the amounts equivalent to these taxes are then transferred to the HTF. Monthly transfers are made based on estimates and are later adjusted on the basis of actual tax receipts, as shown in the figure.
Apportionment
Federal legislation requires generally that funds paid into the HTF be returned to the states for various highway program areas in accordance with legislatively established formulas. Prior to the Moving Ahead for Progress in the 21st Century Act (MAP-21) enacted in 2012, each apportioned highway program funded by the HTF had its own formula for distribution, and the total amount of Federal assistance a State received was the sum of the amounts it received for each program. Additionally, a set of complex procedures dictated the method for apportioning HTF funding among the states. MAP-21 required FHWA to divide the total authorized amount among the states in the following manner:
- In FY13, the state receives the same total apportionment that it received in FY12.
- In FY14, the state receives a total apportionment share equal to the state's share of FY12 formula funds. The resulting total apportionment is adjusted, if necessary, to ensure that the state receives at least 95% of the dollar amount of its contributions to the Highway Account of the HTF.
As under MAP-21, the Fixing America's Surface Transportation (FAST) Act, enacted in late 2015, and the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law (BIL), enacted in 2021, authorizes a single amount for each year for all apportioned highway programs combined. That amount is apportioned among the States, and then each State's apportionment is divided among the individual apportioned programs.
Resources
Funding Federal-aid Highways
This FHWA publication typically has been updated following the enactment of new highway or surface transportation acts. The report explains the funding of Federal-aid highways and follows the financial process from inception in an authorization act to payment from the HTF, and includes discussion of the congressional and Federal agency actions that occur throughout. This January 2017 update of the report incorporates changes in funding procedures brought about by MAP-21 and the FAST Act.
MAP-21 Apportionment of Federal Highway Tax Revenues
FAST Act Apportionment of Federal Highway Tax Revenues
BIL Apportionment of Federal Highway Tax Revenues
Further detail on the apportionment process is found on FHWA's MAP-21 and FAST Act websites.
Highway
Statistics (published annually)
These publications are prepared by the FHWA Office of Highway Policy Information presenting and analyzing statistics of general interest on motor fuel, motor vehicles, driver licensing, highway-user taxation, state highway finance, highway mileage, and Federal aid for highways. They also include highway finance data for municipalities, counties, townships, and other units of local government.


